- Course No E – 2095
- PDH Units: 3
No data found for Custom Course Number
No data found for Custom Course Units
Intended Audience: Energy, Mechanical and Environmental Engineers.
PDH UNITS: 3
LNG plants and other petrochemical plants are built to bring a return on investment to their investors through their safe operation. Their designers and engineer-led operators require technical knowledge to ensure these facilities are safe and dependable. This training covers LNG technologies at both a technical and human resource development level. This training is needed to help you design, operate, and maintain an LNG facility; however, many LNG topics can also apply to other petrochemical plants. It is intended to give the learner the intermediate technical knowledge needed to make informed planning, maintenance, and operating decisions to ensure plant safety, reliability, and efficiency. In the ten lessons, details will be given on the operation of an LNG plant, refrigeration systems for liquefying, and the thermodynamics involved in producing, storing, transporting, and re-vaporizing LNG. This is the seventh of the ten lessons. The topics covered in this lesson include understanding:
- The volatility and behavior of zeotropic mixtures (components of LNG)
- The relationship between various LNG components' molecular mass, volatility, and temperature.
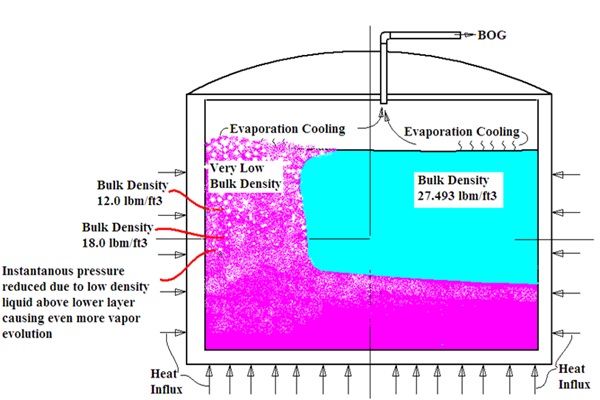
- The weathering of LNG that does not contain nitrogen, including its effect on LNG density
- The weathering of LNG that does contain nitrogen, including its effect on LNG density
- In-tank convective currents of LNG with and without nitrogen in the LNG
- The impact of hydrogen injected into LNG liquefier feed gas.
- The FERC guidelines on higher heating value, wobbe number, and inerts on interchangeability.
- Understanding LNG blending and sendout stabilization.
- Nitrogen-induced rollover phenomenon.
- Removal of nitrogen from LNG before storage.
- Removal of hydrogen from LNG before storage.
- The phenomenon of hydrogen stress corrosion cracking
Learning Objectives
This is the seventh in a series of ten progressively more in-depth courses on Liquefied Natural Gas. Although this learning focuses on LNG facilities, many concepts also apply to other petrochemical plants. This course introduces the learner to the technical topics related to the production, storage, transportation, and vaporization of Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). It should be considered an Intermediate-Level course. The learning objectives of the complete ten learning sessions are to understand at an intermediate level the following:- Understanding how to safely, reliably, and efficiently operate an LNG plant
- General characteristics of LNG and safety
- Liquefaction pretreatment,
- Liquefaction systems,
- LNG tanks, valves, pumps, vaporizers, auxiliaries, and other LNG plant equipment.
- BOG management and plant operations
- Transporting LNG
- Efficient operation of LNG facilities
- Importance of philosophies, procedures, maintenance, and modes of operation.
- Understanding the thermodynamic relationship that governs the behavior of zeotropic hydrocarbons.
- Zeotropic fluid volatility behavior of H2, N2, CH4, C2H6, C3H8 etc.
- Interchangeability
- Segregating Inventories
- Properties of N2
- Properties of H2
- Effects of N2 in feed gas on liquefaction systems
- Effects of H2 in feed gas on liquefaction systems
- Effects of N2 on LNG storage
- Effects of H2 on LNG storage
- Effects of N2 on BOG
- Effects of H2 on BOG
- Removal of N2 and H2 from Feed Gas and from LNG
- Hydrogen Stress Corrosion Cracking Concerns
Once completed, your order and certificate of completion will be available in your profile when you’re logged in to the site.