Subtotal: $4.99
TP – 1257 An Introduction to Principles of Carbon Adsorption for Waste Treatment for Professional Engineers
$4.99
Description
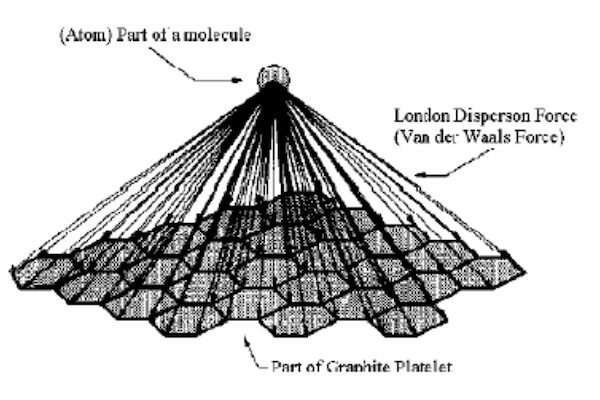
Activated carbon can be manufactured from carbonaceous material, including coal (bituminous, subbituminous, and lignite), peat, wood, or nutshells (i.e., coconut). The manufacturing process consists of two phases, carbonization and activation. The carbonization process includes drying and then heating to separate by-products, including tars and other hydrocarbons, from the raw material, as well as to drive off any gases generated. The carbonization process is completed by heating the material at 400–600°C in an oxygen-deficient atmosphere that cannot support combustion.


 TP - 1107 An Introduction to Design of Building Envelopes for Professional Engineers
TP - 1107 An Introduction to Design of Building Envelopes for Professional Engineers