-
×
 E - 1162 Fly Ash for Highway Engineers
1 × $175.00
E - 1162 Fly Ash for Highway Engineers
1 × $175.00 -
×
 E - 1592 Fundamentals of Signalized Intersections
1 × $125.00
E - 1592 Fundamentals of Signalized Intersections
1 × $125.00 -
×
 E - 2065 Ethics - Practicing Engineering with an Invalid License
1 × $75.00
E - 2065 Ethics - Practicing Engineering with an Invalid License
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1721 Aging in Place – Eliminating Traps
1 × $100.00
E - 1721 Aging in Place – Eliminating Traps
1 × $100.00 -
×
![[Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment](data:image/png;base64,iVBORw0KGgoAAAANSUhEUgAAASwAAAEsAQAAAABRBrPYAAAAAnRSTlMAAHaTzTgAAAAiSURBVGje7cExAQAAAMKg9U9tCj+gAAAAAAAAAAAAAAB4GS20AAH/6QlrAAAAAElFTkSuQmCC) [Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment
1 × $99.00
[Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment
1 × $99.00 -
×
 E - 1169 Energy Storage for Solar and Wind Power
1 × $125.00
E - 1169 Energy Storage for Solar and Wind Power
1 × $125.00 -
×
 E - 1144 Residential Deck Construction
1 × $75.00
E - 1144 Residential Deck Construction
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
1 × $75.00
E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
1 × $100.00
E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1111 Disinfection with Peroxone
1 × $50.00
E - 1111 Disinfection with Peroxone
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1101 Solar Energy Fundamentals
1 × $100.00
E - 1101 Solar Energy Fundamentals
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1570 Sustainable Transportation Control Measures
1 × $75.00
E - 1570 Sustainable Transportation Control Measures
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1141 Engineering Ethics-NSPE Code of Ethics for Engineers
1 × $50.00
E - 1141 Engineering Ethics-NSPE Code of Ethics for Engineers
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1109 Design of Small Water Systems
1 × $150.00
E - 1109 Design of Small Water Systems
1 × $150.00 -
×
 E - 1873 HVAC Chilled Beam Systems
1 × $100.00
E - 1873 HVAC Chilled Beam Systems
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1743 Composting Toilet Construction Guide
1 × $50.00
E - 1743 Composting Toilet Construction Guide
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1156 Methods for Cleaning of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater
1 × $125.00
E - 1156 Methods for Cleaning of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater
1 × $125.00 -
×
 E - 1133 Energy Conservation in Industrial and Commercial Environment
1 × $200.00
E - 1133 Energy Conservation in Industrial and Commercial Environment
1 × $200.00 -
×
 E 1102 Valve Fundamentals
1 × $100.00
E 1102 Valve Fundamentals
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1110 Ponds – Planning, Design, and Construction
1 × $150.00
E - 1110 Ponds – Planning, Design, and Construction
1 × $150.00 -
×
 E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00 -
×
 E - 1105 Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts
1 × $100.00
E - 1105 Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1543 Steel Bridge Maintenance and Repair
1 × $75.00
E - 1543 Steel Bridge Maintenance and Repair
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 2008 In-situ Load Testing – The Legal Requirements and Practicalities
1 × $60.00
E - 2008 In-situ Load Testing – The Legal Requirements and Practicalities
1 × $60.00 -
×
 E - 1544 ADA Update: A Primer for Small Business
1 × $25.00
E - 1544 ADA Update: A Primer for Small Business
1 × $25.00 -
×
 E - 1199 Renewable Electricity Futures Study-Grid Effect
1 × $175.00
E - 1199 Renewable Electricity Futures Study-Grid Effect
1 × $175.00 -
×
 E - 1201 DOE Smart Grid: an Introduction
1 × $150.00
E - 1201 DOE Smart Grid: an Introduction
1 × $150.00 -
×
 E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
1 × $50.00
E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1560 Antiterrorism Assumptions for Building Design
1 × $75.00
E - 1560 Antiterrorism Assumptions for Building Design
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1545 ADA Update: A Primer for State and Local Government
1 × $25.00
E - 1545 ADA Update: A Primer for State and Local Government
1 × $25.00 -
×
 E - 1140 Engineering Ethics- Ethics Guidelines for Professional Conduct
1 × $50.00
E - 1140 Engineering Ethics- Ethics Guidelines for Professional Conduct
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1913 Energy Saving in Pump, Fan and Cooling Tower
1 × $75.00
E - 1913 Energy Saving in Pump, Fan and Cooling Tower
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1911 Internet of Things (IoT) Application and Future Challenges
1 × $50.00
E - 1911 Internet of Things (IoT) Application and Future Challenges
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1909 Finite Element Method for Heat Transfer Problems
1 × $75.00
E - 1909 Finite Element Method for Heat Transfer Problems
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
1 × $75.00
E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1555 OSHA Guide for Protecting Roofing Workers
1 × $25.00
E - 1555 OSHA Guide for Protecting Roofing Workers
1 × $25.00 -
×
 E - 1124 Fuel Cells–Green Power
1 × $75.00
E - 1124 Fuel Cells–Green Power
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1912 Waste Heat Recovery
1 × $50.00
E - 1912 Waste Heat Recovery
1 × $50.00 -
×
 E - 1579 Alternative Uses of Highway Right of Way
1 × $125.00
E - 1579 Alternative Uses of Highway Right of Way
1 × $125.00 -
×
 E - 1753 Coastal Construction: Identifying Hazards
1 × $125.00
E - 1753 Coastal Construction: Identifying Hazards
1 × $125.00 -
×
 E - 1713 Construction Project Management
1 × $100.00
E - 1713 Construction Project Management
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1556 Using CHP at Wastewater Treatment Facilities
1 × $75.00
E - 1556 Using CHP at Wastewater Treatment Facilities
1 × $75.00
Subtotal: $3,934.00


 E - 1162 Fly Ash for Highway Engineers
E - 1162 Fly Ash for Highway Engineers  E - 1592 Fundamentals of Signalized Intersections
E - 1592 Fundamentals of Signalized Intersections  E - 2065 Ethics - Practicing Engineering with an Invalid License
E - 2065 Ethics - Practicing Engineering with an Invalid License  E - 1721 Aging in Place – Eliminating Traps
E - 1721 Aging in Place – Eliminating Traps ![[Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment](https://nciteengineeringhub.com/wp-content/uploads/water-treatment-300x300.jpg) [Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment
[Live Webinar] Basics of Water Treatment  E - 1169 Energy Storage for Solar and Wind Power
E - 1169 Energy Storage for Solar and Wind Power  E - 1144 Residential Deck Construction
E - 1144 Residential Deck Construction  E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems  E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel  E - 1111 Disinfection with Peroxone
E - 1111 Disinfection with Peroxone  E - 1101 Solar Energy Fundamentals
E - 1101 Solar Energy Fundamentals  E - 1570 Sustainable Transportation Control Measures
E - 1570 Sustainable Transportation Control Measures  E - 1141 Engineering Ethics-NSPE Code of Ethics for Engineers
E - 1141 Engineering Ethics-NSPE Code of Ethics for Engineers  E - 1109 Design of Small Water Systems
E - 1109 Design of Small Water Systems 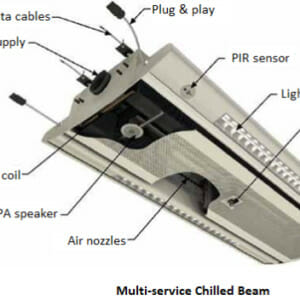 E - 1873 HVAC Chilled Beam Systems
E - 1873 HVAC Chilled Beam Systems  E - 1743 Composting Toilet Construction Guide
E - 1743 Composting Toilet Construction Guide  E - 1156 Methods for Cleaning of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater
E - 1156 Methods for Cleaning of Contaminated Soils and Groundwater  E - 1133 Energy Conservation in Industrial and Commercial Environment
E - 1133 Energy Conservation in Industrial and Commercial Environment  E 1102 Valve Fundamentals
E 1102 Valve Fundamentals  E - 1110 Ponds – Planning, Design, and Construction
E - 1110 Ponds – Planning, Design, and Construction  E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course  E - 1105 Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts
E - 1105 Flow Measurement in Pipes and Ducts  E - 1543 Steel Bridge Maintenance and Repair
E - 1543 Steel Bridge Maintenance and Repair  E - 2008 In-situ Load Testing – The Legal Requirements and Practicalities
E - 2008 In-situ Load Testing – The Legal Requirements and Practicalities  E - 1544 ADA Update: A Primer for Small Business
E - 1544 ADA Update: A Primer for Small Business  E - 1199 Renewable Electricity Futures Study-Grid Effect
E - 1199 Renewable Electricity Futures Study-Grid Effect  E - 1201 DOE Smart Grid: an Introduction
E - 1201 DOE Smart Grid: an Introduction  E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers  E - 1560 Antiterrorism Assumptions for Building Design
E - 1560 Antiterrorism Assumptions for Building Design  E - 1545 ADA Update: A Primer for State and Local Government
E - 1545 ADA Update: A Primer for State and Local Government  E - 1140 Engineering Ethics- Ethics Guidelines for Professional Conduct
E - 1140 Engineering Ethics- Ethics Guidelines for Professional Conduct  E - 1913 Energy Saving in Pump, Fan and Cooling Tower
E - 1913 Energy Saving in Pump, Fan and Cooling Tower  E - 1911 Internet of Things (IoT) Application and Future Challenges
E - 1911 Internet of Things (IoT) Application and Future Challenges  E - 1909 Finite Element Method for Heat Transfer Problems
E - 1909 Finite Element Method for Heat Transfer Problems  E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels  E - 1555 OSHA Guide for Protecting Roofing Workers
E - 1555 OSHA Guide for Protecting Roofing Workers  E - 1124 Fuel Cells–Green Power
E - 1124 Fuel Cells–Green Power 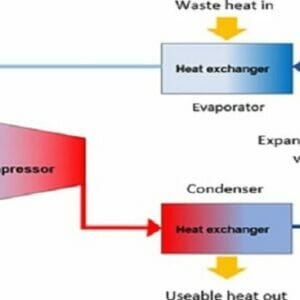 E - 1912 Waste Heat Recovery
E - 1912 Waste Heat Recovery  E - 1579 Alternative Uses of Highway Right of Way
E - 1579 Alternative Uses of Highway Right of Way  E - 1753 Coastal Construction: Identifying Hazards
E - 1753 Coastal Construction: Identifying Hazards  E - 1713 Construction Project Management
E - 1713 Construction Project Management  E - 1556 Using CHP at Wastewater Treatment Facilities
E - 1556 Using CHP at Wastewater Treatment Facilities