Subtotal: $100.00
E – 1781 Heat Tracing Systems
$100.00
Courses Included
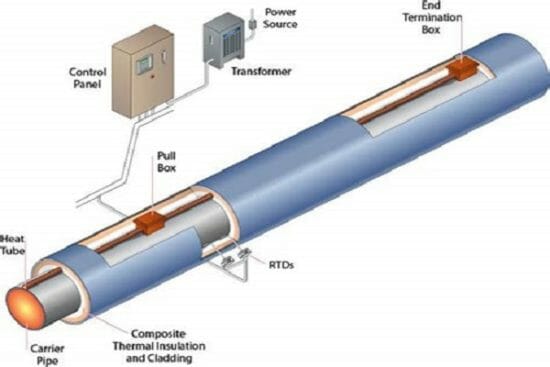
The term heat-tracing refers to the continuous or intermittent application of heating pipelines, tanks, vessels or other equipment used for storage or transportation of a product (liquid, powder or gas). The purpose of heat tracing is to compensate or make up for the heat loss to the surrounding atmosphere in low ambient temperature climates. Some applications for heat tracing include; preventing fluid from freezing, maintaining process fluids at pumpable viscosities, preventing formation of hydrates and waxes in hydrocarbon liquids (oil, etc) and also sometimes to preheat part of a fluid system prior to initial startup or after a primary heating system shutdown.
The heat tracing is generally accomplished by employing electric tracing, or steam tracing and insulating both the process fluid pipe and the tracer together, using appropriate insulation materials and metal lagging. The decision between electric and steam heat tracing depends on various factors and this 4 hour course outlines the pros and cons of both the methods.


 E - 1525 Biodiesels- Handling and Use Guide
E - 1525 Biodiesels- Handling and Use Guide