- Course No.: E – 1995
- PDH Units: 3
No data found for Custom Course Number
No data found for Custom Course Units
Intended Audience: Civil & Structure Engineers.
PDH UNITS: 1
The objective of this course is to assist a licensed design professional, forensic structural engineers, consulting engineers or/and a licensed general contractor to deeply know, and understand the analysis, design & construction of post-tension slabs.
Learning Objectives:
At the successful conclusion of this course, you will learn the following knowledge and skills:- How does post tension slab work?
- Main component of post tensioning
- PT slab construction steps
- Advantages & disadvantages of post tension slabs
- Post-tension type
- Strength of pre-stressing steel
- Design stepsin details
- Loading conditions
- Definition of member forces
- Post-tension slab construction procedure
- Design flow chart for post-tension
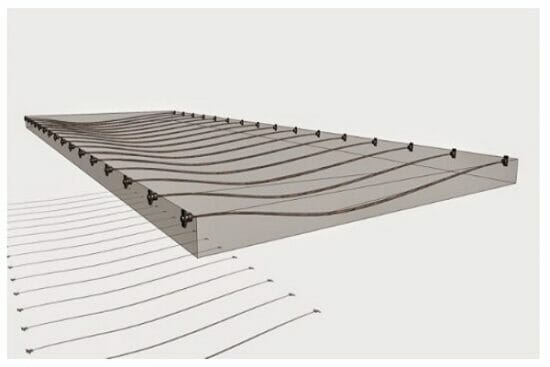
- Tendon profile type
- Howto arrange tendon of parabolic shape?
- Check finalstresses and check initialstresses
- Steps to calculate & check stresses in simple beam
- Stress distribution according to tendon arrangement
- What are pre-stress losses? & check pre-stress losses
- Kinds and calculation of losses
- How to calculate and check flexural strength
- How to calculate and check shear strength
- Detailed example of one-way shear capacity of solid slab continuous over 2 equal spans
- Major differences between normal and post-tension slabs
Once completed, your order and certificate of completion will be available in your profile when you’re logged in to the site.
Ethics Courses
Course No.: E - 1995
PDH Units: 3