- Course No E – 1818
- PDH Units: 5
No data found for Custom Course Number
No data found for Custom Course Units
- Course No E – 1818
- PDH Units: 5
Intended Audience: HVACl & Mechanical Engineers
Credits: 5 PDH Units
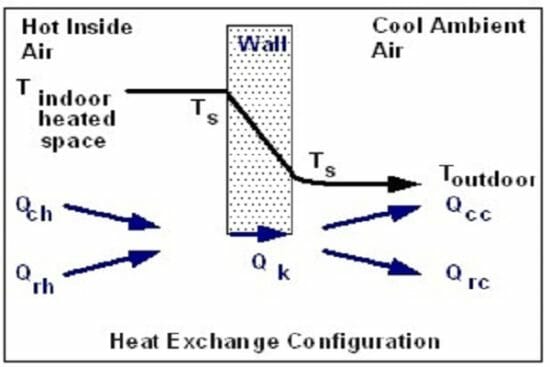
The prime requirement in respect of the indoor climate in a building is that room temperature should be at a comfortable level, regardless of the weather conditions outside. As soon as the ambient temperature is lower than the indoor temperature, heat flows out from the building through its boundary surfaces (the building envelope). At the same time, the building also loses heat through air infiltration, i.e. the inward leakage of outdoor air into the building through gaps and cavities in walls, roofs, doors and windows. Bearing in mind the fact that the indoor temperature in most buildings is maintained at a little over 65°F, this means, throughout most of the year, the building is losing heat to its surroundings. This 5-hour course, discusses the stepwise procedure to determine the rate of heat loss through building elements using a process called heat loss calculation. You will learn how to extrapolate your calculation of a maximum hourly rate into an annual energy usage rate. You will also learn some useful tips on saving heating energy. The course includes one sample example for better understanding of the concept.
Learning Objectives:
At the successful conclusion of this course, you will learn the following knowledge and skills:- Describe the factors affecting comfort in winter
- Describe the overall heat transfer coefficient (U-value) and its relationship to resistance (R-value)
- Understand the basic equation of heat loss through building elements such as walls, roof and glass
- Understand the basic equation of heat loss through floor slab and basement
- Understand the basic equation of heat loss through ventilation and infiltration
- Understand the concept of degree days and how it is used to estimate the annual heat loss
- Understand the three basic modes of heat transfer, conduction, convection and radiation
- Understand the difference between the k-values, C-values, R-values and U-values
- Learn by examples to calculate the series resistance and U-values of a composite wall
- Learn how to determine the infiltration and ventilation air flow rate
- Understand by an example the detailed methodology to heat loss calculations
- Understand the basic terminology and definitions related to air conditioning load calculations
Course Reviews
5
- 5 stars2
- 4 stars0
- 3 stars0
- 2 stars0
- 1 stars0
Once completed, your order and certificate of completion will be available in your profile when you’re logged in to the site.










Excellent Review Course
Great info