-
×
 E - 1816 Dos & Don’ts In Steel And Connection Design
1 × $80.00
E - 1816 Dos & Don’ts In Steel And Connection Design
1 × $80.00 -
×
 E - 1443 OSHA: Ground-Fault Protection on Construction Sites
1 × $25.00
E - 1443 OSHA: Ground-Fault Protection on Construction Sites
1 × $25.00 -
×
 E - 1959 Remove and Replace a Bridge - Infrastructure Projects - Construction Technology
1 × $25.00
E - 1959 Remove and Replace a Bridge - Infrastructure Projects - Construction Technology
1 × $25.00 -
×
 E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
1 × $75.00
E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1935 Engineering Ethics: The Millennium Tower Sinking and Tilting-Was the Root Cause Engineering Ethics Violations?
1 × $100.00
E - 1935 Engineering Ethics: The Millennium Tower Sinking and Tilting-Was the Root Cause Engineering Ethics Violations?
1 × $100.00 -
×
 E - 1951 Damping in structures. The different approaches adopted in Seismic and Wind Engineering and a new unifying theme
1 × $95.00
E - 1951 Damping in structures. The different approaches adopted in Seismic and Wind Engineering and a new unifying theme
1 × $95.00 -
×
 E - 1125 Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pump Basics
1 × $75.00
E - 1125 Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pump Basics
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1895 ISO 50001 -Energy Management
1 × $75.00
E - 1895 ISO 50001 -Energy Management
1 × $75.00 -
×
 E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00 -
×
 E - 1891 Steel Bridges- Redundancy in Design
1 × $75.00
E - 1891 Steel Bridges- Redundancy in Design
1 × $75.00
Subtotal: $825.00


 E - 1816 Dos & Don’ts In Steel And Connection Design
E - 1816 Dos & Don’ts In Steel And Connection Design  E - 1443 OSHA: Ground-Fault Protection on Construction Sites
E - 1443 OSHA: Ground-Fault Protection on Construction Sites  E - 1959 Remove and Replace a Bridge - Infrastructure Projects - Construction Technology
E - 1959 Remove and Replace a Bridge - Infrastructure Projects - Construction Technology  E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems
E - 1444 Operation and Maintenance of Landfill Gas Systems  E - 1935 Engineering Ethics: The Millennium Tower Sinking and Tilting-Was the Root Cause Engineering Ethics Violations?
E - 1935 Engineering Ethics: The Millennium Tower Sinking and Tilting-Was the Root Cause Engineering Ethics Violations? 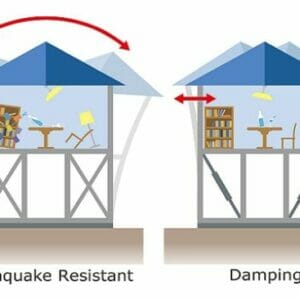 E - 1951 Damping in structures. The different approaches adopted in Seismic and Wind Engineering and a new unifying theme
E - 1951 Damping in structures. The different approaches adopted in Seismic and Wind Engineering and a new unifying theme  E - 1125 Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pump Basics
E - 1125 Centrifugal and Positive Displacement Pump Basics  E - 1895 ISO 50001 -Energy Management
E - 1895 ISO 50001 -Energy Management  E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course  E - 1891 Steel Bridges- Redundancy in Design
E - 1891 Steel Bridges- Redundancy in Design