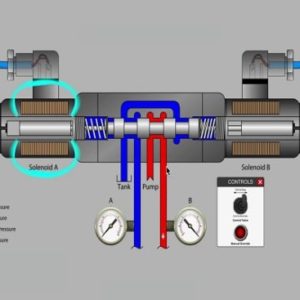
Description
This course provides an introduction to impressed current cathodic protection systems. There are two principle methods of providing cathodic protection: sacrificial anode and impressed current. The primary advantage of impressed current cathodic protection systems over sacrificial anode cathodic protection systems is that the driving potential of the impressed current systems is not limited by the corrosion potential of an active metal. The ability to select appropriate driving potentials, and to adjust the driving potential after system installation, gives the designer and operator of impressed current cathodic protection systems additional flexibility to compensate for changing environmental conditions. The primary advantage of this variable driving potential in the design of impressed current cathodic protection systems is the ability to select the location of anode beds for an optimum distribution of protective current with a minimum of interference. The variable driving potential available in impressed current systems also allows the protection of structures in high resistivity environments where the output of sacrificial anodes is severely limited. The primary operational benefit of variable driving potential is the ability to adjust the system for changes in soil resistivity, anode condition, structure surface (coating) condition and additions to the structure.
Course Outline
1. INTRODUCTION
2. DETERMINATION OF CIRCUIT RESISTANCE
3. DETERMINATION OF POWER SUPPLY REQUIREMENTS
4. SELECTION OF POWER SUPPLY TYPE
5. RECTIFIER SELECTION
6. ANODES FOR IMPRESSED CURRENT SYSTEMS
7. OTHER SYSTEM COMPONENTS
This course will give professional engineers and other design and construction professionals an introduction to the fundamentals of impressed current cathodic protection systems.
- Learn about the inherent flexibility impressed current systems provide;
- Learn about the importance of anode-to-electrolyte resistance;
- Learn why common practice is to connect several anodes in parallel in a group;
- Learn about special formulas to use for water tanks;
- Learn the importance of backfill in anode installation;
- Learn why the quality of splices and connections is important; and
- Learn about DC power supply alternatives.
 E - 1114 Hydraulic Jumps and Supercritical & Non-uniform Flow
2 × $75.00
E - 1114 Hydraulic Jumps and Supercritical & Non-uniform Flow
2 × $75.00  E - 1107 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
1 × $150.00
E - 1107 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
1 × $150.00  E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
1 × $200.00  E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
1 × $50.00
E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
1 × $50.00  E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
1 × $75.00
E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
1 × $75.00  E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
1 × $100.00
E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
1 × $100.00  E - 1108 Heat Transfer Review for Engineers
1 × $75.00
E - 1108 Heat Transfer Review for Engineers
1 × $75.00 

 E - 1114 Hydraulic Jumps and Supercritical & Non-uniform Flow
E - 1114 Hydraulic Jumps and Supercritical & Non-uniform Flow  E - 1107 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow
E - 1107 Fundamentals of Fluid Flow  E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course
E - 1123 Concrete Methods and principles - Full 8 Hours Course  E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers
E - 1106 Fundamentals of Heat Exchangers  E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels
E - 1117 Introduction to Biofuels  E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel
E - 1103 Hydraulic Design of Storm Sewers with Excel  E - 1108 Heat Transfer Review for Engineers
E - 1108 Heat Transfer Review for Engineers