- Course No E – 1807
- PDH Units: 2
No data found for Custom Course Number
No data found for Custom Course Units
- Course No E – 1807
- PDH Units: 2
Intended Audience: Mechanical, Civil and Environmental Engineers
PDH UNITS: 2
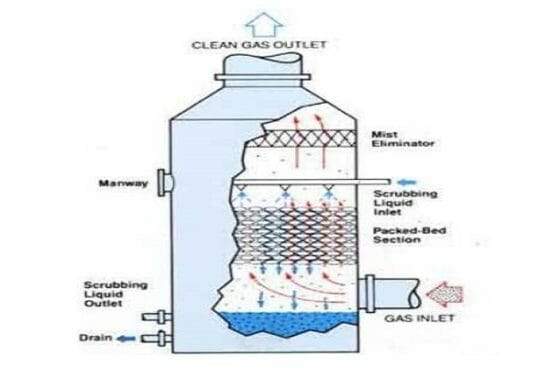
Scrubbers and precipitators are technologies employed in air pollution control. A scrubber utilizes a liquid to separate particulate or gaseous contaminants from gas. Separation is achieved through mass contact of the liquid and gas. Boiler emissions to be controlled include fly ash and sulfur oxides. Incinerator emissions to be controlled include fly ash, sulfur oxides and hydrogen chloride. An electrostatic precipitator is a device which removes particles from a gas stream. It accomplishes particle separation by the use of an electric field which imparts a positive or negative charge to the particle, attracts the particle to an oppositely charged plate or tube, and-removes the particle from the collection surface to a hopper by vibrating or rapping the collection surface. This course will give you technical guidance you can apply scrubber and electrostatic precipitor technology to air postelection control.
Learning Objectives:
At the successful conclusion of this course, you will learn the following knowledge and skills:- Learn about low energy scrubbers which are more efficient at gaseous removal than at particulate removal. A low energy scrubber utilizes a long liquid/gas contact time to promote mass transfer of gas;
- Learn about preformed spray scrubbers (spray tower) which are a device which collects particles or gases on liquid droplets and utilizes spray nozzles for liquid droplet atomization;
- Learn about centrifugal scrubbers which are cylindrical in shape, and impart a spinning motion to the gas passing through them.
- Learn how the spin may come from introducing gases to the scrubber tangentially or by directing the gas stream against stationary swirl vanes;
- Learn about impingement and entrainment scrubbers which employ a shell which holds liquid. Learn how gas introduced into a scrubber is directed over the surface of the liquid and atomizes some of the liquid into droplets;
- Learn about venturi scrubbers that utilize a moving gas stream to atomize and accelerate the liquid droplets;
- Learn about the ejector venturi scrubber that utilizes a high pressure spray to collect particles and move the gas, and how high relative velocity between drops and gas aids in particle collection;
- Learn about two stage electrostatic precipitators (ESP) that are designed so that the charging field and the collecting field are independent of each other, and how the charging electrode is located upstream of the collecting plates. Two stage ESPs are used in the collection of fine mists.
- Learn about single stage ESPs that are designed so that the same electric field is used for charging and collecting particulates; and
- Learn about hot precipitators designed to operate at gas temperatures above 600 degrees Fahrenheit and usually of the single stage, parallel plate design.
Once completed, your order and certificate of completion will be available in your profile when you’re logged in to the site.